Theta Waves: The Complete Guide (2026)
Share
Neuroscience · Theta Waves
A clear, research-informed guide to theta brainwaves — what they are, what they do, and how to activate theta states through meditation, relaxation, and modern neurotechnologies.
Written for wellness practitioners, meditators, clinicians, and individuals seeking calm, focus, and emotional balance.
Theta Waves
Theta waves (4–7 Hz) are one of the most intriguing and influential brainwave states. They are associated with deep relaxation, creativity, emotional processing, memory formation, and the early stages of sleep. In recent years, theta waves have become a major area of interest for people who want to improve their stress regulation, support cognitive performance, or deepen their meditation practice.
This guide brings together the best current knowledge on theta waves — including how they work, why they matter, and how to encourage healthy theta activity using both natural practices and non-invasive neurotechnologies such as Audio-Visual Entrainment (AVE) and Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES).
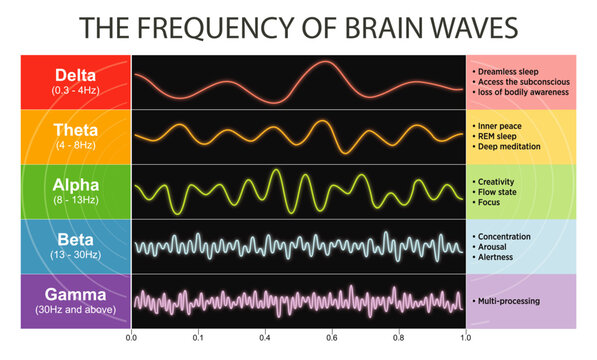
1. What Are Theta Waves?
Theta waves are rhythmic electrical patterns within the 4–7 Hz frequency range, observed through EEG. They naturally appear during:
- early-stage sleep
- deep meditation
- creative flow states
- daydreaming and visualization
- memory formation and emotional integration
Many people search for “what are theta waves” because they feel moments of calm or insight during meditation but don’t know what’s happening in the brain. Theta is a transitional state — not fully awake, not fully asleep — where the mind becomes quieter and more internally focused.
2. What Theta Waves Do to the Brain
Research suggests that theta waves support several essential brain functions:
- emotional processing — integrating thoughts and feelings
- creativity — divergent thinking and big-picture insight
- memory encoding — especially spatial and long-term memory
- stress reduction — lower physiological arousal
- relaxation and calm — shift away from high-beta “stress mode”
People often describe theta as the state where ideas “click,” intuition increases, or deep calm becomes accessible.

3. The Benefits of Theta Waves
Ahrefs shows a strong search interest in “theta waves benefits” and related terms. The most commonly reported benefits include:
- Deep relaxation and reduced stress load
- Enhanced creativity and problem-solving
- Improved emotional regulation
- Easier access to meditative states
- Support for sleep transitions
- Better mental clarity after deep rest
4. Theta Waves and Sleep
“Theta waves sleep” is another major search topic. Theta plays a key role in falling asleep and transitioning through the early sleep stages. When the brain can’t naturally downshift into theta, people often report:
- racing thoughts
- difficulty winding down
- trouble falling asleep
- light, fragmented sleep
Supporting theta activity — through behavior, relaxation, or guided brainwave entrainment — may help smooth this transition.
5. How to Activate Theta Brain Waves
Many readers search for “how to activate theta brain waves.” Here are evidence-informed ways to invite more theta activity naturally:
1. Guided Meditation
Slow breathing, body scans, and visualization naturally promote theta rhythms.
2. Breathwork
Techniques like box breathing or extended exhales help quiet high-beta activity.
3. Relaxation Rituals Before Sleep
Dim light, reduced screen time, and slow-paced routines ease the shift into theta.
4. Audio-Visual Entrainment (AVE)
AVE introduces rhythmic light and sound pulses to encourage theta frequencies. For a deeper explanation, see the AVE + CES deep dive.
5. Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback trains people to increase or regulate theta activity through real-time EEG feedback. Learn more in this guide to neurofeedback at home.
6. Structured Entrainment Devices
Non-invasive systems that combine AVE and CES — such as the DAVID series — offer sessions specifically designed to support theta and alpha transitions. Compare systems at Find Your DAVID.
6. Theta Waves, 4 Hz, and “Theta Tracks”
A subset of searchers look for specific frequencies, like “theta waves 4 Hz” or “theta tracks 4hz.” The lower end of theta (around 4–5 Hz) is often associated with:
- deep meditative absorption
- calming pre-sleep states
- slow emotional integration
Different frequencies within theta may feel slightly different, but the broader range (4–7 Hz) is most important for wellness and cognitive support.
7. Are Theta Waves Safe?
A common question: “Is theta brain waves dangerous?” For healthy individuals, theta states are a normal part of daily brain function — especially during meditation and sleep.
Theta can feel unfamiliar for people who are constantly in high-beta (fight-or-flight), but it is not inherently dangerous. As with any wellness approach, those with neurological conditions should consult a clinician before using stimulation-based technologies.
8. Can AVE Help Increase Theta Waves?
Audio-Visual Entrainment (AVE) uses rhythmic pulses of light and sound to gently guide brainwaves toward calm, coherent rhythms. Research suggests AVE can support:
- alpha-theta transitions
- reduced stress arousal
- improved mood regulation
- more consistent meditation states
For scientific background, see: Scientific Studies on DAVID Devices
For a complete technical overview: AVE + CES Effects
To find the right system: Find Your DAVID
9. Theta Waves vs. Other Brainwaves
Google users often compare theta to alpha or beta. Here’s a clear overview:
- Theta vs Alpha: Theta = deeper relaxation and internal focus; Alpha = calm, alert relaxation.
- Theta vs Beta: Beta = concentration and problem-solving; too much beta = stress and overthinking.
- Theta vs Gamma: Gamma = high-level integration and insight; occurs during peak moments.
10. Building a Theta-Supporting Lifestyle
If your goal is to regularly access theta for creativity, calm, or emotional clarity, consider the following routine:
- daily slow-breathing or mindfulness
- short pre-sleep relaxation rituals
- limiting evening screen stimulation
- regular meditation practice
- structured AVE sessions (alpha/theta programs)
- journaling after theta-based sessions for integration
Explore Natural Brainwave Entrainment
If you're curious about structured ways to support alpha and theta states, explore the DAVID systems and their evidence-informed programs.
Learn About AVE Systems